Let’s imagine for a moment that you’re a skilled artist with a vivid imagination and a friend comes to you with a peculiar request.
She says, “Can you draw me a two-story house that looks like a giant cupcake?”
On the one hand, you have all the skills to draw this from scratch, it just needs a bit of time and creativity. On the other hand, time is precious — and so are you!
But what if you had an artificial intelligence model help you create this exact image in under 1 minute from just the description alone?
It sounds like something straight out of a sci-fi movie, but this is the reality of AI image generators like Midjourney, Stable Diffusion, and DALL·E 2.
Case in point — this took 45 seconds:

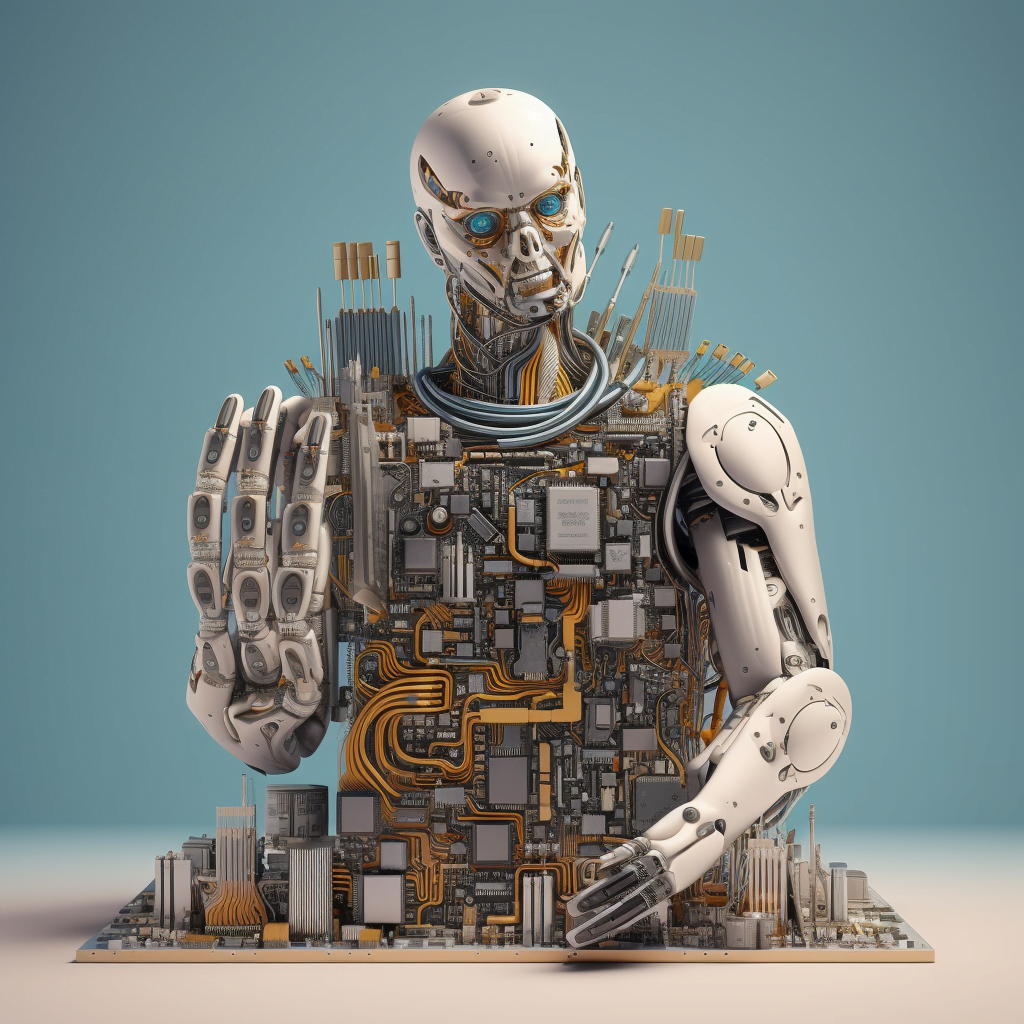
These fascinating AI tools have the power to turn textual descriptions into creative, detailed images. They can create pictures of things that don’t exist, yet they are surprisingly realistic. It’s like having a digital artist at your disposal, ready to sketch out your wildest ideas.
But how do these Artificial intelligence image generators work? Let’s dive into the mesmerizing world of AI and unravel the magic behind it.
How Do AI Image Generators like Midjourney Work?
Imagine you’re in a giant library. This isn’t your ordinary library, though.
Instead of books, it’s filled with billions of images. Each image is a bit of knowledge, a small piece of the visual world. This is what we call an artificial neural network, the brain of AI image generators. It’s a system modeled after the human brain, designed to recognize patterns and learn from experience.
At the heart of the neural network is a process called machine learning.
Think of it as teaching a child how to recognize different objects. You’d show them a picture of a cat and say, “This is a cat.” After showing them enough pictures of cats, they’ll start recognizing them on their own. That’s essentially how machine learning works, but on a much larger and more complex scale.
In the case of AI image generators, they’re trained using a vast array of images, not just thousands, but millions and millions of images. They learn to recognize shapes, colors, and textures, all the different elements that make up a picture.
They don’t just understand what a cat looks like, but also what a cupcake-shaped house might look like.
The magic happens when you feed the AI a description. It searches its library of learned images and starts to piece together the picture bit by bit, much like a jigsaw puzzle. It might start with the shape of a house, add the roundness of a cupcake, and finally, add the details that make it look like a delicious treat.
Most of these top AI models then go through a process called ‘reinforcement learning from human feedback‘, or RLHF for short.
What is Reinforcement Learning From Human Feedback?

There’s a technique called reinforcement learning from human feedback that helps computers learn how to make better decisions. It’s like teaching a new puppy to learn how to sit by giving it treats, instead, it’s having a computer to do something by giving it feedback and rewards.
Here’s how it works.
Instead of just telling the computer what’s right and wrong, we ask real people to rank different examples of the computer’s behavior and output. These rankings then help us score the computer’s results. Then we use a special technique called a “reward model” that predicts if the output is good or bad.
RLHF is really useful when we want computers to understand and use human language. As I’m sure you can imagine, it’s hard for computers to learn language tasks on their own because the rewards are often tricky to define or measure. But RLHF helps computers generate answers that match our complex human values, understanding, and preferences.
It also helps them give more detailed responses and avoid answering questions they shouldn’t, I’m sure you’ve seen plenty of angry examples in the news.
What is the Technology Behind Midjourney, Stable Diffusion, and DALL·E 2?
When we talk about AI image generators, Midjourney, Stable Diffusion, and DALL·E 2 are top of the line. They take the basic principles we’ve discussed and add their own unique twist.
Midjourney shines in its ability to create transitional images. It’s like watching an artist sketch, erase, and redraw elements of a picture until it’s just right. It uses a process called ‘generative adversarial network‘ (GAN). This involves two neural networks – one that generates the image (the artist), and one that critiques it (the art critic).
They work together until the image fits the description provided.
Stable Diffusion, on the other hand, uses a method called ‘diffusion models‘. It starts with a random image, then gradually changes it, step by step, until it matches the description. It’s a bit like sculpting from a block of marble, chipping away bit by bit until you have a beautiful statue.
Lastly, the first version of DALL·E used something called a ‘discrete Variational Auto-Encoder‘ (dVAE), a computer program that learns from examples to generate new things, like pictures or music, but specializes in creating things that belong to specific categories or options.
For instance, the model can make pictures of different animals, with each picture representing a specific animal category, by understanding the patterns and features of existing examples and using that knowledge to create new ones that fit within those categories.
OpenAI‘s newer, far more powerful version, DALL·E 2, takes things a step further by being able to generate images from complex descriptions, creating original, realistic images and art by combining various concepts, attributes, and styles using a similar technique as Stable Diffisuion, a diffusion model.
What About Safety and Ethics in AI Image Generation?

With such powerful capabilities, it’s important to consider the ethical implications of these hugely popular AI image generators. Midjourney reportedly has roughly 15 million users, DALL·E has 1.5 million, and Stable Diffusion has 10 million. These represent a huge number of creators, each possibly making dozens of images a day or far more for super-users.
The implication of their potential impact on society is even larger.
Imagine the potential for misinformation, like when hyper-realistic photos of Trump and Putin being arrested spread like wildfire online, only to be revealed they were created in Midjourney. As this technology advances, the line between the unreal and real will continue to blur, with AI-generated images, audio, and video becoming just as common as genuine content—but able to be created in a tiny fraction of the normal time and cost.
To prevent some of the harmful use cases of their AI tools, companies like OpenAI have put safety measures in place.
For example, DALL·E 2 has been designed to limit the generation of violent, hateful, or adult images. Its exposure to explicit content during training was minimized, and advanced techniques were used to prevent photorealistic generations of real individuals’ faces, including those of public figures. It uses filters to identify and block attempts to violate these policies, and it employs both automated and human monitoring systems to guard against misuse.
Midjourney has implemented a unique combination of text-based AI filtering combined with human curation to limit their tool from being abused too much.
These precautions help ensure that AI image generators are used responsibly, making the digital world a safer place, although they certainly aren’t without their controversy, especially against free-speech advocates. Midjourney, for example, banned users from making images about China’s president, Xi Jinping, the only leader on their banned words list to be included.
AI is Transforming the Creative Process
The mesmerizing world of AI image generators, with prominent examples like Midjourney, Stable Diffusion, and DALL·E 2, represents a tremendous leap forward in the way we create and visualize concepts. These models utilize machine learning techniques to turn textual descriptions into vivid, detailed images in a way that was once unimaginable.
While the technology is new and the entire AI industry reminds us of the crypto or NFT crazes (and certainly scams are bound to come), one of the biggest impacts will be on how society accepts, rejects, and handles the advent of this amazing technology.
As we continue to explore and harness the power of these tools, we are reshaping the very nature of the creative process. While challenges remain, the potential for these AI tools to unlock new levels of creativity and efficiency in art and design is profound, marking a significant milestone in our journey towards the AI-augmented future.
Personally, I plan on riding the wave and creating more cool things than I ever dreamed of.
Happy prompting!